MongoDB Tutorial 4: Overview of MongoDB
MongoDB consists of a set of databases. Each database again consists of Collections. Data in MongoDB is stored in collections. The below figure depicts the typical database structure in MongoDB.
Database
Database in MongoDB is nothing but a container for collections. We will learn how to create a new Database, drop a Database and how to use an existing Database in the coming lessons.
Collections
- Collection is nothing but a set of MongoDB documents. These documents are equivalent to the row of data in tables in RDBMS. But, collections in MongoDB do not relate to any set schema as compared to RDBMS. Collections are a way of storing related data. Being schemaless, any type of Document can be saved in a collection, although similarity is recommended for index efficiency. Document's can have a maximum size of 4MB.
- We can use namespace to logically group and nest collections. For example : There can be one collection named
db.studytonight.usersto save user informations, then there can be others likedb.studytonight.forum.questionsanddb.studytonight.forum.answersto store forum questions and answers respectively. - If we create an Index on a namespaced collection, it will only apply on that namespace only. We will learn later in this tutorial, how to create indexes.
- A collection is physically created as soon as the first document is created in it.
- You must be wondering why create multiple collections with different namespace, when we can keep any form or data in a single collection itself. It's because, MongoDB does not index attributes for totally unrelated documents. So it is advised to keep related data in collections.
Documents
Document in MongoDB is nothing but the set of key-value pairs. These documents will have dynamic schema which means that the documents in the same collection do not need to possess the same set of fields.
Since MongoDB is considered as a schema-less database, each collection can hold different type of objects. Every object in a collection is known as Document, which is represented in a JSON like (JavaScript Object Notation) structure(nothing but a list of key-value pair). Data is stored and queried in BSON, its binary representation of JSON-like data. You can know more about BSON format from this webpage → BSON Specification and BSON Types
Sample Data in MongoDB
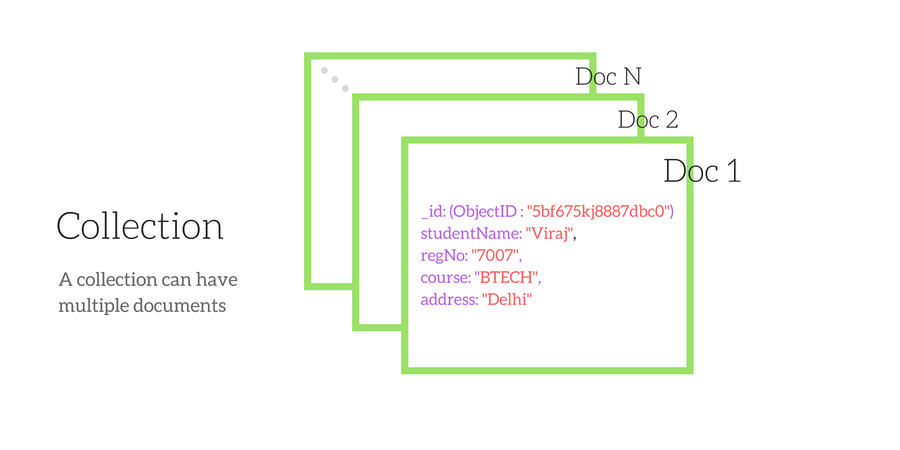
Note: In the above figure, the field
_id represents the primary key identifier of the given document. MongoDB also stores the values in the form of arrays of value as well. Infact any type of data can be stored as values, and nothing requires to be pre-defined. In other words, you do not have to predefine the type of data to be stored, you can store anything you want. Remember, MongoDB is schema-less.
Documents are not identified by a simple ID, but by an object identifier type. The default Id is a combination of machine identifier, timestamp and process id to keep it unique, but user can changes it to anything.
Example of Array as value
{ _id : 112233,name : "Viraj",education : [{year : 2029,course : "BTECH",college : "IIT, Delhi"},{year : 2031,course : "MS",college : "Harvard College"}]}
Example of Different Datatypes in one Document
The value of fields in a document can be anything, including other documents, arrays, and arrays of documents, date object, a String etc.
var mydoc = {_id : ObjectId("5099803df3f4948bd2f98391"),name : { first: "Alan", last: "Turing" },birth : new Date('Jun 23, 1912'),death : new Date('Jun 07, 1954'),contribs : [ "Turing machine", "Turing test", "Turingery" ],view : NumberLong(1250000)}

Comments
Post a Comment